Steps to File for Divorce in India
Divorce in India is governed by various personal laws depending on the religion of the parties involved. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Understand the Grounds for Divorce
Different personal laws in India define specific grounds for divorce. Some common grounds include:
- Adultery
- Cruelty
- Desertion
- Impotency
- Mental Disorder
- Irretrievable Breakdown of Marriage (recognized in limited cases)
- Mutual Consent Divorce (simpler and faster).
Step 2: Consult a Lawyer
It’s crucial to seek legal advice from an experienced family lawyer. A lawyer can:
- Guide you through the specific personal laws applicable to you.
- Draft your divorce petition in accordance with legal requirements.
- Help you gather the necessary documents.
Step 3: Gather Necessary Documents
Prepare and organize essential documents, such as:
- Marriage certificate.
- Proof of residence.
- Evidence supporting your grounds for divorce (photos, emails, medical reports, etc.).
- Details of joint assets or liabilities.
- Proof of income for alimony/child support considerations.
Step 4: File the Divorce Petition
- Where to File: File the petition in the appropriate family court, which is usually located in the jurisdiction where:
- The marriage took place.
- The couple last resided together.
- Either party is currently residing.
- Types of Divorce:
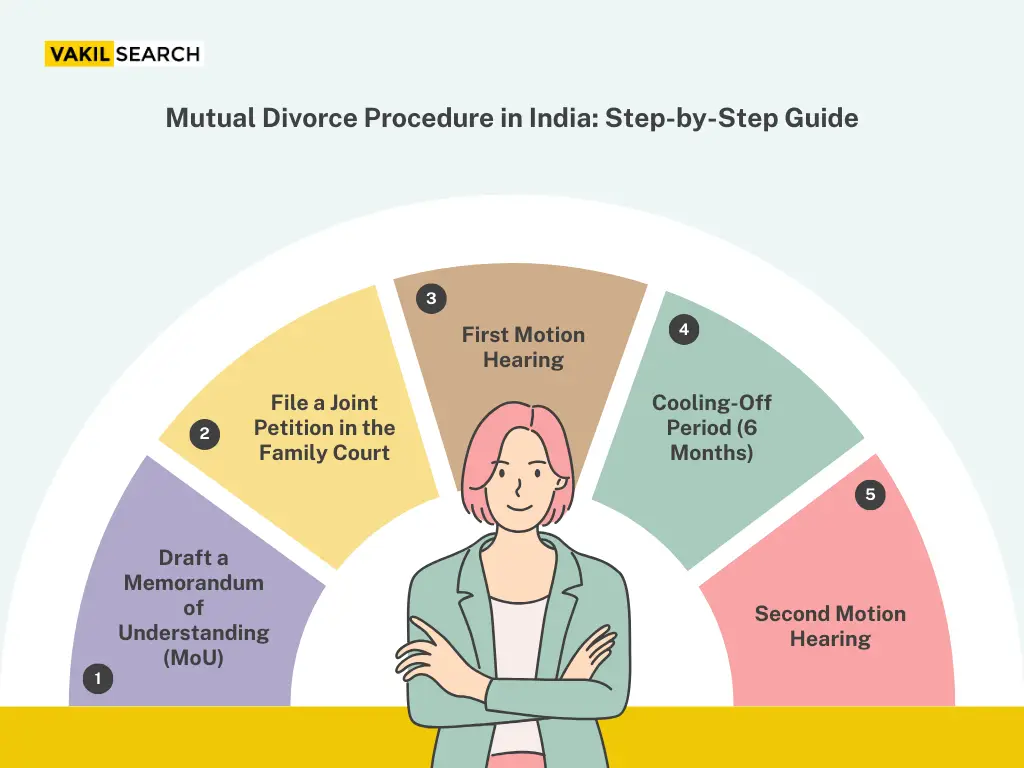
- Mutual Consent Divorce: Both parties agree to the separation. Typically resolved within 6 months.
- Contested Divorce: Filed when one party does not consent or disputes exist. This process can be lengthy.
Step 5: Attend Court Hearings
- Once the petition is filed, the court will:
- Summon both parties for hearings.
- Mediate (if necessary) to explore reconciliation options.
- Hear arguments and evidence in contested cases.
- In the case of mutual consent, both parties must confirm their agreement in two stages: one at the filing and another after a mandatory cooling-off period of 6 months.
Step 6: Follow the Court’s Orders
- For mutual consent divorce, if no disputes arise, the court will grant the decree of divorce.
- For contested divorce, the court may:
- Award alimony/maintenance.
- Decide on child custody and visitation rights.
- Resolve property disputes.
Step 7: Obtain the Divorce Decree
Once the court issues the divorce decree, it legally dissolves the marriage. Keep this document safely as proof of your divorce.
Additional Tips:
- Try Mediation First: Courts often encourage couples to resolve their disputes amicably through mediation or counseling.
- Know Your Rights: Understand your rights regarding alimony, child custody, and property division.
- Be Patient: Contested divorces can take years due to legal complexities and backlogged courts.
4o


